Bootstrap Breakpoints Usage
Introduction
Getting in consideration all of the feasible display widths where our online pages could ultimately display it is essential to form them in a manner providing universal sharp and powerful look-- typically employing the help of a efficient responsive framework like easily the most famous one-- the Bootstrap framework which most current edition is currently 4 alpha 6. However what it really handles to help the webpages pop up fantastic on any type of display screen-- why don't we have a look and see.
The main standard in Bootstrap normally is adding some system in the countless practical device display screen sizes ( or else viewports) placing them in a number of varieties and styling/rearranging the content correctly. These particular are in addition termed grid tiers or display screen dimensions and have developed quite a bit throughout the various variations of the most prominent currently responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4.
The ways to use the Bootstrap Breakpoints Responsive:
Generally the media queries become specified with the following structure @media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~. The conditions are able to limit one end of the interval such as min-width: 768px of each of them just like min-width: 768px - meantime the viewport width in within or same to the values in the demands the rule applies. Considering that media queries belong the CSS language certainly there can possibly be a lot more than one query for a single viewport width-- if so the one particular being really checked out by the browser last has the word-- much like regular CSS rules.
Huge differences of Bootstrap versions
In Bootstrap 4 compared with its predecessor there are 5 display screen widths however given that the current alpha 6 build-- simply 4 media query groups-- we'll return to this in just a sec. Considering that you most likely realize a .row within bootstrap incorporates column elements keeping the actual page web content which can surely span up to 12/12's of the detectable size offered-- this is simplifying but it's one more thing we are actually speaking about here. Each and every column element get defined by one of the column classes incorporating .col - for column, display scale infixes determining down to which display screen size the web content will stay inline and will span the entire horizontal width below and a number demonstrating how many columns will the element span when in its own display screen size or above.
Screen sizes
The display screen dimensions in Bootstrap typically utilize the min-width condition and come like follows:
Extra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like col-6 - such element for example will span half width no matter the viewport.
Extra small-- sizes less than 576px-- This display screen certainly doesn't come with a media query yet the designing for it rather gets utilized just as a usual rules getting overwritten due to the queries for the widths just above. What's as well fresh within Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it simply does not utilize any kind of dimension infix-- and so the column style classes for this particular screen dimension get defined just like col-6 - such element for example will span half size despite of the viewport.
Small screens-- applies @media (min-width: 576px) ... and the -sm- infix. { For example element having .col-sm-6 class will certainly cover half width on viewports 576px and larger and full width below.
Medium displays-- makes use of @media (min-width: 768px) ... as well as the -md- infix. As an example element coming with .col-md-6 class is going to span half width on viewports 768px and larger and total width below-- you've possibly got the drill currently.
Large display screens - utilizes @media (min-width: 992px) ... as well as the -lg- infix.
And at last-- extra-large screens - @media (min-width: 1200px) ...-- the infix here is -xl-
Responsive breakpoints
Since Bootstrap is undoubtedly designed to be mobile first, we make use of a number of media queries to develop sensible breakpoints for user interfaces and styles . These types of Bootstrap Breakpoints Responsive are normally built upon minimum viewport widths and also help us to graduate up elements when the viewport changes.
Bootstrap basically makes use of the following media query ranges-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass files for style, grid system, and elements.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Due to the fact that we prepare source CSS in Sass, all of media queries are readily available through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We from time to time use media queries that move in the some other course (the supplied display screen size or even scaled-down):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthAgain, these kinds of media queries are in addition obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are also media queries and mixins for aim a single segment of display screen sizes employing the minimum and maximum Bootstrap Breakpoints Working sizes.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These types of media queries are as well accessible through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Equally, media queries may well cover numerous breakpoint widths:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for focus on the same screen scale selection would be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Conclusions
Together with specifying the width of the web page's items the media queries come about all over the Bootstrap framework usually getting specified simply by it - ~screen size ~ infixes. Whenever discovered in several classes they have to be interpreted just like-- regardless of what this class is handling it is definitely handling it down to the screen size they are pertaining.
Check a number of video short training regarding Bootstrap breakpoints:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap breakpoints formal records"

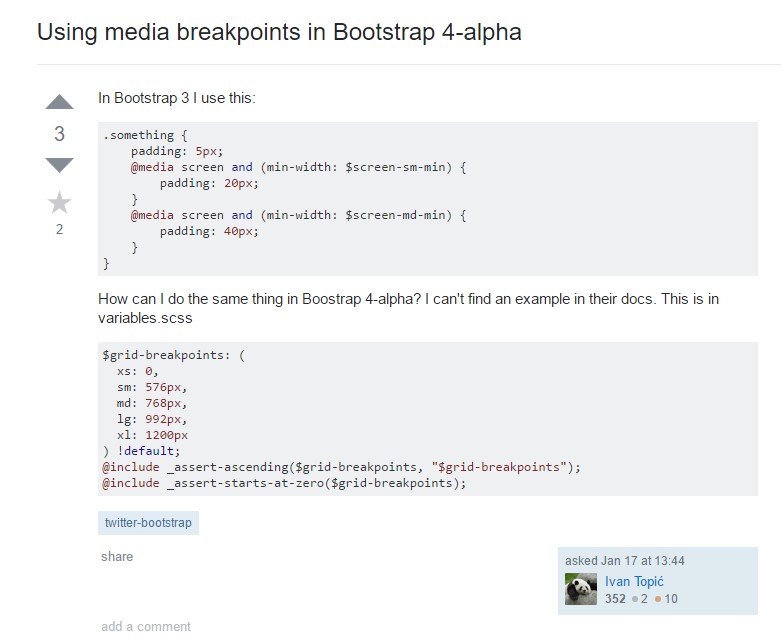
Bootstrap Breakpoints issue
Transform media query breakpoint systems from em to px